What Are Connectivity Protocols?
Connectivity protocols are the technologies that enable smart home devices to communicate with each other and with your hub, smartphone, or voice assistant. They are the "language" your devices use to send commands and share information.
The four main connectivity protocols in smart homes are:
1. Wifi
2. Zigbee
3. Z-wave
4. Bluetooth
Why Are Connectivity Protocols Important?
Choosing the right protocol for your smart home is critical because:
Compatibility
Not all devices work together; understanding protocols helps you avoid compatibility issues.
Performance
Some protocols are better for specific tasks, like handling many devices or reducing energy use.
Reliability
A strong and consistent connection ensures your devices work seamlessly.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each protocol, you can design a system that meets your needs.
Wifi
What It Is
Features | Specs |
|---|---|
Frequency | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz (newer routers also support 6 GHz - Wi-Fi 6E) |
Range per device | 30-50 meters (100-165 feet) indoors (depends on router strength and walls) |
Max devices per network | Limited by router capacity (many routers struggle beyond ~50 devices) |
Data speed | Up to 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6), 600 Mbps - 1 Gbps (Wi-Fi 5) |
Power consumption | High (not ideal for battery-powered devices) |
Network type | Point-to-point (devices connect directly to the router, not to each other) |
Best For
Pros
Cons
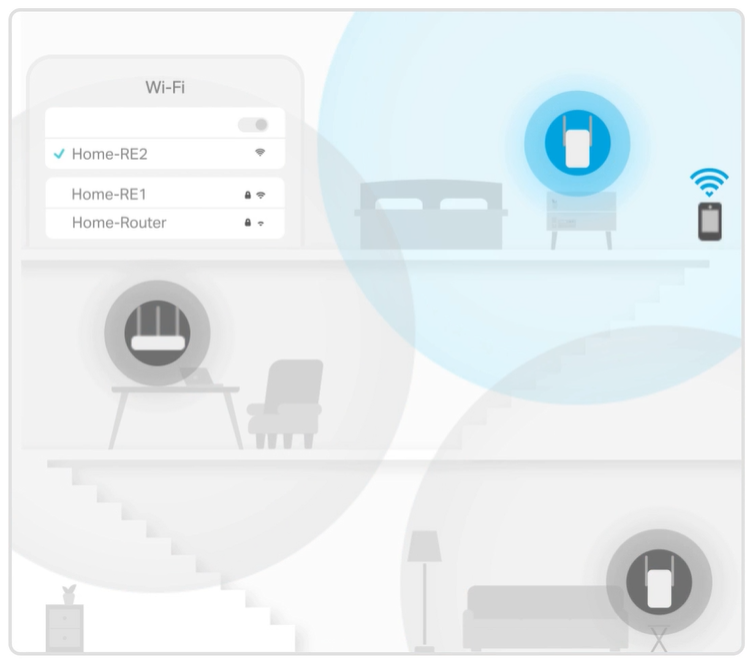
Traditional router struggles with limited WiFi coverage
Nugget
Upgrade to a mesh Wi-Fi system for better coverage if you have dead zones or a large home.
Zigbee
What It Is
Technical Specs
Features | Specs |
|---|---|
Frequency | 2.4 GHz (globally) |
Range per device | 10-20 meters (33-66 feet) |
Max devices per network | 65,000+ |
Data speed | 250 kbps |
Power consumption | Very low (ideal for battery-powered devices) |
Network type | Mesh (devices relay signals to extend range) |
Best For
Pros
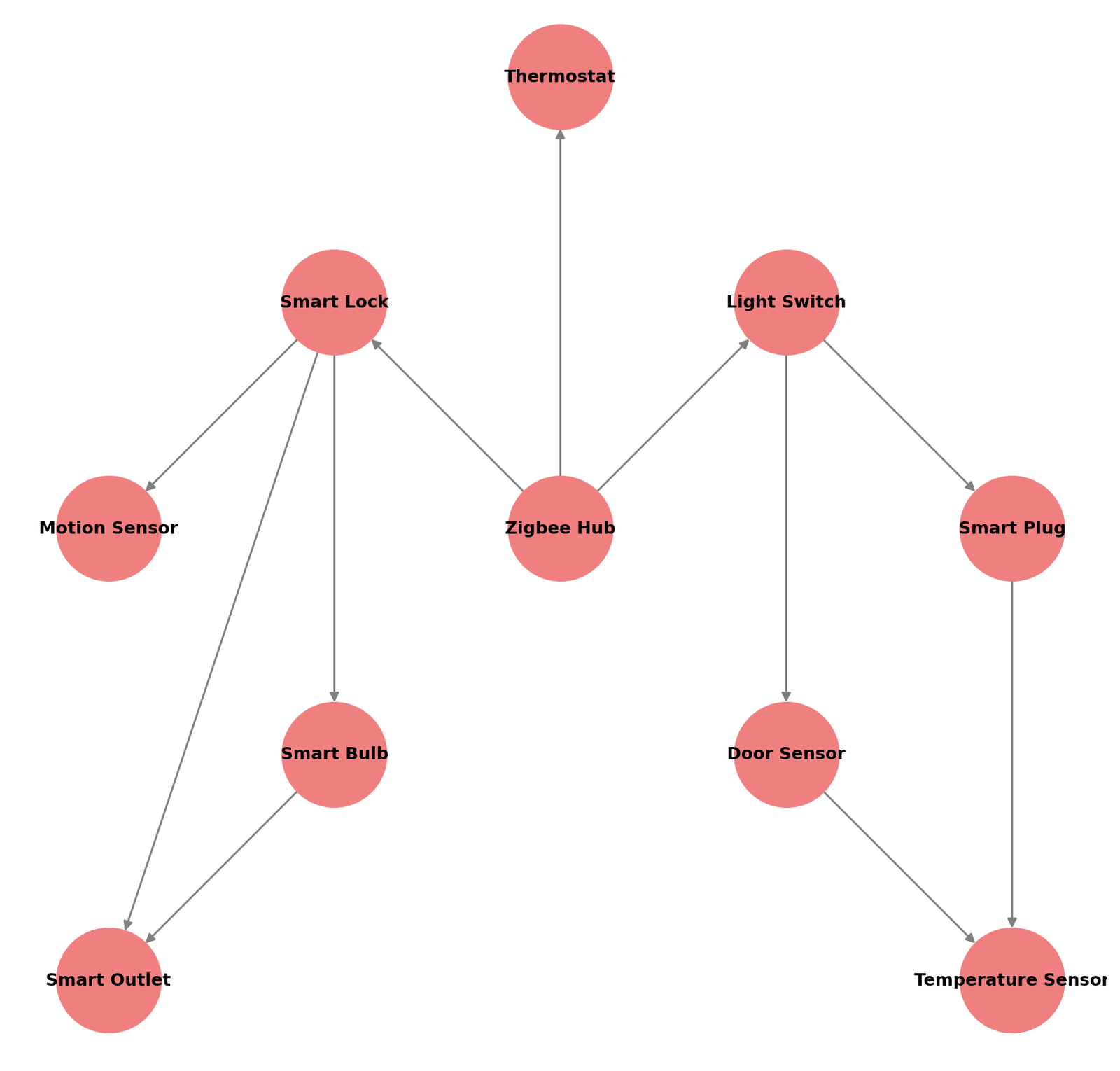
Zigbee network with more devices and dense mesh
Cons
Nugget
Look for hubs that support Zigbee and work with multiple brands.
Z-Wave
What It Is
Features | Specs |
|---|---|
Frequency | 908 MHz (U.S.), 868 MHz (Europe) (varies by region) |
Range per device | 30-100 meters (100-328 feet) (better than Zigbee) |
Max devices per network | 232 |
Data speed | 100 kbps (slower than Zigbee but more stable) |
Power consumption | Low (ideal for battery-powered security devices) |
Network type | Mesh (devices relay signals to extend range) |
Best For
Pros
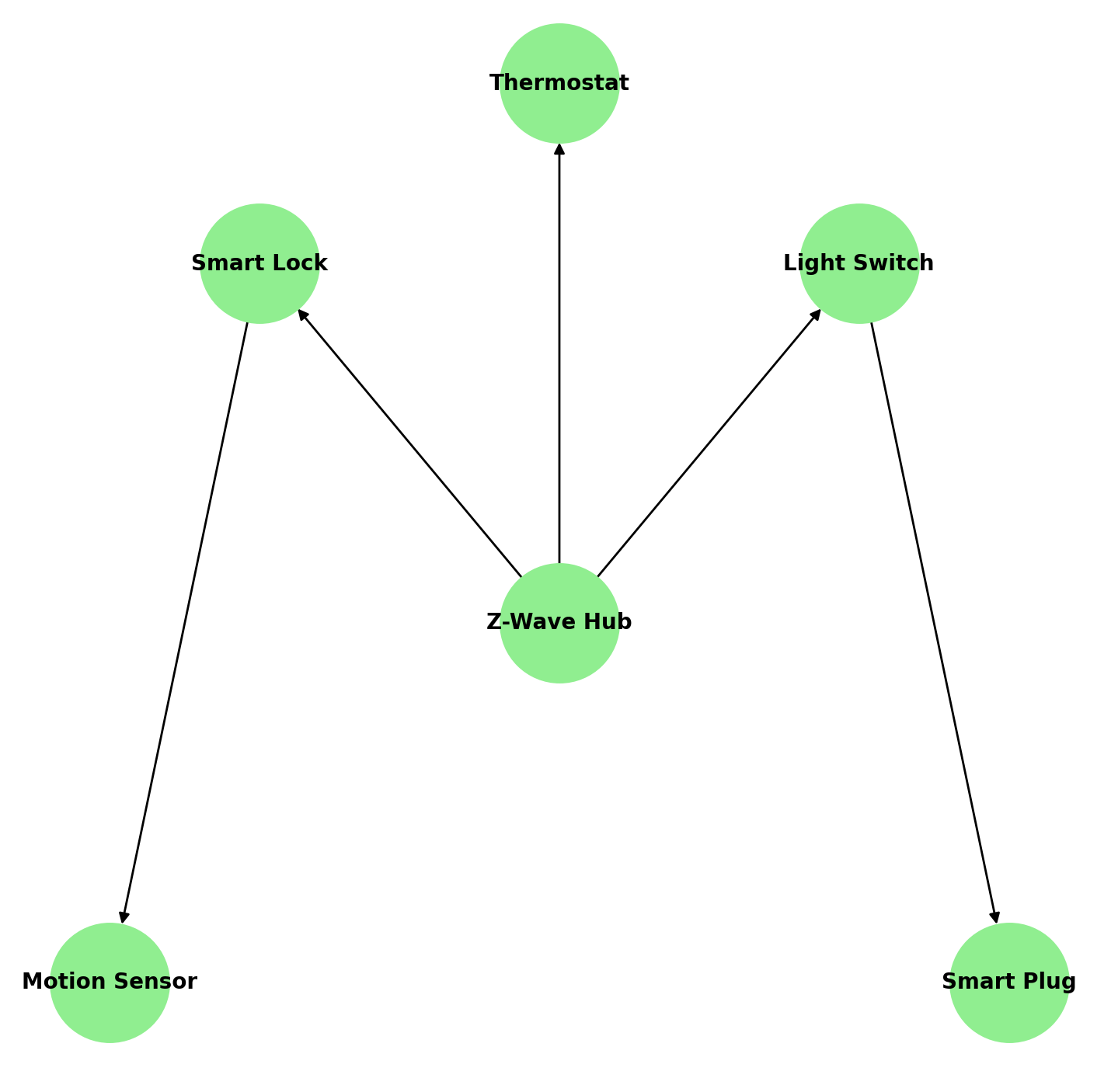
Z-Wave network with long range and fewer devices
Cons
Nugget
Choose Z-Wave for robust, secure networks where range is critical (e.g., larger homes or detached garages).
Bluetooth
What It Is
Features | Specs |
|---|---|
Frequency | 2.4 GHz |
Range per device | 10 meters |
Max devices per network | Limited |
Data speed | 1-3 Mbps (Bluetooth 4.2), up to 50 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.0 & 5.2) |
Power consumption | Low (but still higher than Zigbee or Z-Wave for constant connections) |
Network type | Point-to-point (Bluetooth Classic) |
Best For
Pros
Cons
Nugget
Use Bluetooth for specific devices that don’t need to communicate with others, like a smart lock on your front door.
Pro Tip
Combine Protocols for Optimal Performance.
Example: Use Wi-Fi for high-bandwidth devices. Then, use Bluetooth for localised control of standalone devices like curtain motors. Finally, use Zigbee or Z-wave for the rest of devices.